What is a matrix ?
A matrix is collection of numbers arranged into a fixed number of rows and columns . Usually the numbers are real numbers. In general, matrices can contain complex numbers but we won't see those here. It can be written in either [ ] or ( ). Here is an example of a matrix with m rows and n columns :

The elements in a matrix A are denoted by aij , where i is the row number and j is the column number . The size of matrix is written : mxn
Types of Matrices
Matrices are distinguished on the basis of their order, elements and certain other conditions.There are several types of matrices but most commonly used are following :
1. Row Matrix :
A matrix is said to be a row matrix if it has only one row.
e.g. A= [7 -0.8 4 -2]
2. Column Matrix :
A matrix is said to be a row matrix if it has only one column.
e.g.
e.g.
3. Square Matrix :
A matrix is said to be square matrix if it has no of rows is equal to no of columns i.e. m=n . Its order is m for m*n matrix.
e.g.
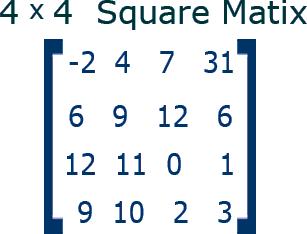
4. Null Matrix :
A matrix is said to be null matrix if all its elements are zero. It is also known as zero matrix.
e.g.

5. Diagonal Matrix :
A square matrix is said to be diagonal matrix if at least one element of principal diagonal is non-zero and all the other elements are zero, that is, square a matrix A= [Aij]n × n is said to be diagonal matrix if aij=0 ,when i≠j.
e.g.
Determinant of a diagonal matrix is multiplication of diagonal elements.
6. Scalar Matrix :
A diagonal matrix is said to be a scalar matrix if all the elements in its principal diagonal are equal to some non-zero constant ,that is a scalar matrix A=[Aij]nxn is said to be a scalar matrix if
- aij=0 ,when i≠j
- aij=k ,when i=j ,for some constant k.
7. Identity/ Unit Matrix :
A diagonal matrix is said to be identity if all of its diagonal elements are equal to one ,denoted by I.
e.g.
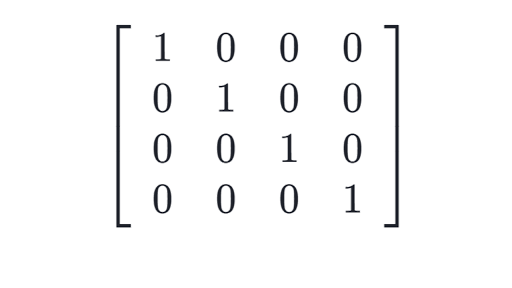
8. Upper Triangular Matrix :
An upper triangular matrix is square matrix where all the elements located below the diagonal are zeros.
e.g.
9. Lower Triangular Matrix :
A lower triangular matrix is square matrix where all the elements located above the diagonal are zeros.
e.g.
Note: We can calculate determinant of lower/upper triangular matrix by multiplication of diagonal matrix .
10. Orthogonal Matrix :
A square matrix is said to be an orthogonal matrix if the multiplication of a matrix and transpose of that matrix is equal to the identity matrix i.e. AA^T=I
11. Idempotent Matrix :
A square matrix is said to be an idempotent matrix if A^2=A.
12. Involuntary Matrix :
A square matrix is said to be an involutary matrix if A^2=I .
13. Symmetric Matrix :
A square matrix is said to symmetric matrix if transpose of a matrix is equal to that (original) matrix , i.e A^T=A or aij=aij .
14. Skew Symmetric Matrix:
A square matrix is said to be Skew Symmetric Matrix if transpose of a matrix is equal to the negative of the original matrix , i.e. A^T=-A or aij=-aji .
15. Singular Matrix :
A square matrix is said to be singular matrix if determinant of matrix is equal to zero,|A|=0 .
16. Non-Singular Matrix :
A square matrix is said to be non-singular matrix if determinant of matrix is not equal to zero, i.e. |A|≠0 .
17. Hermitian Matrix :
A square matrix is said to be hermitian matrix if conjugate of transpose of matrix is equal to the original matrix .
18. Skew Hermitian Matrix :
A square matrix is said to be skew hermitian matrix if conjugate of transpose of matrix is equal to the negative of original matrix.
Good explanation bro
ReplyDelete